Dr Saadia Farooqui, Consultant from the Paediatric Ophthalmology & Adult Strabismus Department at Singapore National Eye Centre (SNEC), shares the warning signs of children's eye problems and when to see an eye doctor.
Your child’s vision plays a crucial role in their development, learning abilities and overall health.
Symptoms of childhood eye condition can be obvious at times and subtle at other times.
“The first seven to eight years of life are important for visual system development in a child. Any impediment to vision during this critical period, if left untreated, may lead to long term vision impairment," said Dr Saadia Farooqui, Consultant from the
Paediatric Ophthalmology & Adult Strabismus Department at
Singapore National Eye Centre (SNEC), a member of the
SingHealth group.
"Early detection is thus crucial so that these conditions can be treated adequately,” she added.
8 Common early warning signs of child vision problems
Here are some tips to spot the warning signs of poor vision in a child:
1. Blinking or rubbing

Frequent blinking or rubbing is an important warning sign to look out for. It could indicate that your child is experiencing unclear vision, eye strain or fatigue, which could stem from a number of vision problems and conditions.
The most common problem experienced is irritation caused by allergies or irritants. Foreign bodies such as pollen or dust entering the eye or triggered allergies can cause irritation of the eye and thus lead to excessive rubbing or blinking.
Possible causes:
Excessive blinking or rubbing can also be a sign of refractive errors such as
myopia. Your child may be experiencing unclear vision which causes them to blink more to focus their sight. An eye check may be necessary to deem if corrective lenses are required.
Eye strain or fatigue is also possible issue. Prolonged periods of screen time, reading or similar activities may overexert the eye.
What to do:
In this case, your child’s screen time should be monitored to provide for necessary breaks to rest their eyes.
2. Eye discomfort or Itchiness
If your child experiences discomfort or itchiness, it is most likely caused by allergies. Exposure to allergens such as pet dander, dust mites, pollen or smoke can make the eyes itchy, watery or red.
Possible causes:
Discomfort of the eye can also be due to eye infections such as conjunctivitis. If your child’s symptoms include redness or eye discharge, it may be signs of
viral or bacterial conjunctivitis.
Other forms of discomfort including headaches or eye pain may indicate eye strain and blurred vision.
What to do:
Monitoring your child’s habits is important to prevent overexertion of their eyes. Check out
this article for tips to prevent eye strain.
3. Crust or goop in eyes
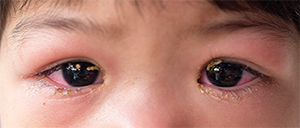
Discharge from your child's eyes or crusty eyes is another sign to look out for. Crusty eyes occur when discharge dries on the eyelids and lashes, and can result from different eye problems or conditions.
Possible causes:
Blepharitis is one common condition. Symptoms include inflammation of the eyelids, redness, itchiness and crust forming around the eye.
A blocked tear duct is another condition that can cause crust to form on the eyelids. The blockage stops tears from draining normally, leading to watery, irritated or infected eyes.
What to do:
You should consult your doctor to obtain the correct diagnosis if this condition persists.
4. Persistent eye watering

Persistent watering of the eyes is a sign to look out for. This may indicate an unusual condition of the eye caused by conjunctivitis or a blocked tear duct.
What to do:
For tips to prevent watery eyes and when to see a doctor, read
this article.
5. Spots or cloudiness in the eye
The appearance of the eye should be monitored to check for anything unusual as it could indicate vision problems.
Possible causes:
Spots on the white of the eye can occur for many different causes, thus the size and colour are important things be noted.
What to do:
In the case of abnormalities arising after an injury, parents are advised to bring their child to see an eye doctor.
Furthermore, eyes that appear grey or cloudy or have an unusual white appearance in photographs should also be a sign to be monitored, as they may be signs of vision problems.
6. Misaligned eyes
Possible causes:
Misaligned eyes is a sign of
strabismus, a disorder where the eyes do not line up in the same direction. Instead, the eyes may be turned inward or outwards, or upward or downwards.
What to do:
If observed in your child, it is important to seek diagnosis and treatment from a doctor as it can cause vision impairment such as double or blurry vision, as the eyes are not focused on the same spot.
Further, if left untreated could develop into
amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, weakening the vision in the misaligned eye.
7. Squinting
Squinting is an effort to focus or make something clearer to view.
Possible causes:
If your child also tends to hold objects close to their face or sits closer to objects such as the television to see, they may be experiencing unclear vision caused by refractive errors such as
myopia.
8. Head tilting or covering an eye
Head tilting or covering an eye to see may also be a sign of unclear vision. The tendency of a child to tilt their head serves to better the angle and improve the clarity of vision.
Possible causes:
This may be caused by problems such as misaligned eyes,
amblyopia, also known as lazy eye, or even a refractive error.
When to bring your child to consult an eye doctor
Regular eye examinations are important. In Singapore, vision screenings are conducted in Primary schools yearly.
If your child fails such a vision screening, it would be wise to see an eye doctor for a full examination.
Additionally,
if your child exhibits some of the above warning signs persistently, it would be best to consult a doctor for a thorough examination.
Ref: G25
Related articles:
Mobile Device Overuse Raises Child Myopia Risk
Doing This Simple Thing Can Help Prevent Child Myopia
What is Lazy Eye (Amblyopia)?
Strabismus (Squint) in Children: How to Treat
FAQs on Common Eye Conditions for Children
