A recent Yahoo
article revealed that a reporter only discovered she had a cancerous growth on her neck after a viewer that spotted her on TV advised her to get it checked. But how common is lymphoma cancer in Singapore and are there other warning signs besides swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck?
Lymphoma in Singapore
According to the Singapore Cancer Registry,
lymphoma ranks the fifth most common cancer among men and sixth most common cancer among women.
Lymphoma cancer: How it happens
Lymphoma cancer is a type of cancer affecting certain types of immune system cells, specifically the white blood cells called lymphocytes B or lymphocytes T.
Lymphocytes travel throughout the body in a clear fluid called lymph. Using a network of vessels that make up the lymphatic system, the lymph passes through small, bean-shaped organs called lymph nodes, which trap harmful substances. Larger clusters of lymph nodes can be found in the neck, armpits and groin.
Read more:
This top cancer (among men and women) is on the rise in young adults
In lymphoma, lymphocytes B or T multiply uncontrollably and fail to die like normal cells eventually would. Patients with lymphoma often notice a swelling of their lymph nodes caused by the formation of painless lumps or tumours. Lymphoma can also occur in other organs as small amounts of lymph and lymph tissue pass through virtually all organs in the body.
“Although the exact causes of lymphoma still remain unknown, it might be related to viruses and infections,” says Prof Lim Soon Thye, Deputy Medical Director (Clinical) and Senior Consultant of the
Division of Medical Oncology at
National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS), a member of the
SingHealth group.
Patients with human immunodeficiency (HIV) infections or on long-term immunosuppressive drugs also have a higher risk of developing lymphoma.
Symptoms of lymphoma
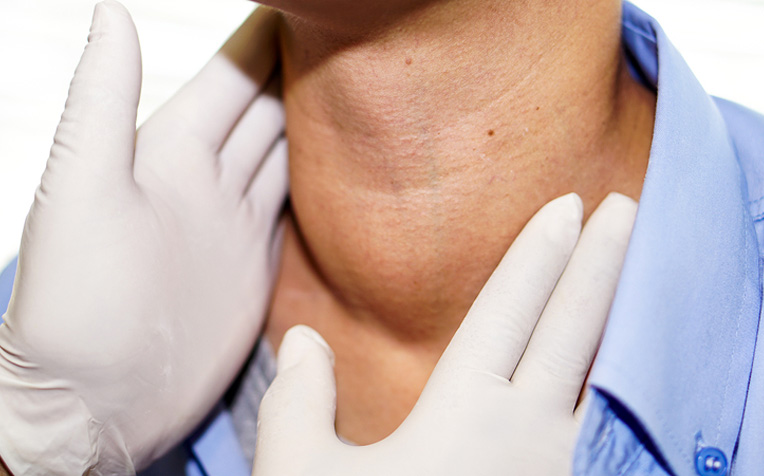
- Painless swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, underarm or groin.
This is the most common symptom
- Persistent fever
- Drenching night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Patchy red skin and itching
- Lack of energy, tiredness or fatigue
Read more: Top foods to eat and avoid when undergoing cancer treatment
Lymphoma cancer can be broadly divided into two categories:
Hodgkin’s lymphoma vs non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Lymphoma cancer can be broadly divided into two categories:
1. Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Patients diagnosed with Hodgkin’s lymphoma (also called Hodgkin’s disease) often have large abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells in their lymph nodes. This disease is highly curable and accounts for about 10 per cent of all lymphoma cases.
Although lymphoma cancer can occur at any age, Hodgkin’s disease is most prevalent in two particular age groups:
- People between 15 and 40 years of age.
- People aged 55 years and above.
2. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (more common)
There are mainly two types of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma:
-
Aggressive (high grade): Tends to grow and spread quickly and cause severe symptoms. If left untreated, it can be fatal within a few months or sooner
-
Slow-growing (low-grade): Tends to grow and spread slowly and cause few symptoms. It is harder to treat and carries a higher risk of relapse
The risk of developing non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma increases with age, with most patients being diagnosed in their 60s.
Read more:
Lymphoma treatment - What are the options?
--
Articles on
HealthXchange.sg are meant for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional surgical, medical or health advice, examination, diagnosis or treatment. Photo courtesy of iStock.