HealthXchange will NEVER ask you to transfer money over a call. If in doubt, call the 24/7 ScamShield helpline at 1799, or visit the ScamShield website at www.scamshield.gov.sg.
Chicken Pox In Adults: Symptoms and Complications
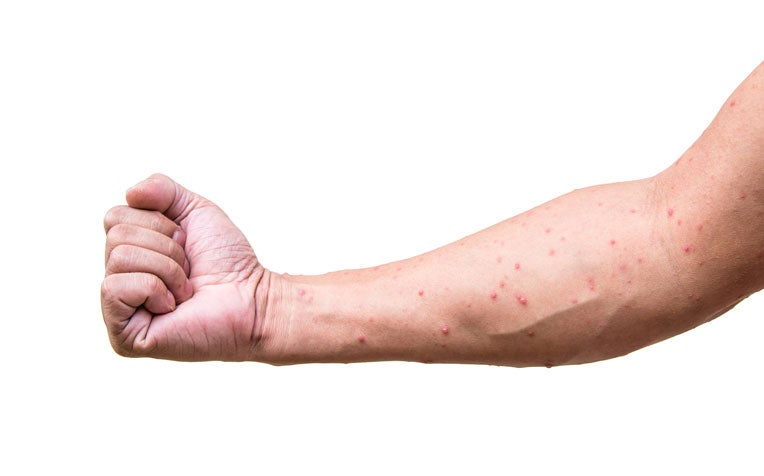
Chicken pox can affect you regardless of age.
Chicken pox may still infect you even if you've had it in the past or have never had it before as a child.
Many of us think of chicken pox (also known as varicella) as the childhood infection that everyone gets once in their lifetime. This isn’t completely true. Adults who have never had chicken pox or received the chicken pox vaccine can still contract the disease. And when this happens, it can cause serious problems.
Equally good to know: if you’ve had chicken pox in the past, you may actually contract it a second time – although it might take a slightly different form.
Chicken pox (or varicella) is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is highly contagious.
“It is transmitted either by contact with the chicken pox rash or by droplets dispersed when an infected person coughs or sneezes,” says Dr Limin Wijaya, Senior Consultant, Department of Infectious Diseases, Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a member of the SingHealth group.
When adults contract chicken pox, there is a greater risk of developing complications. This is especially so for people with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, previous organ or bone marrow transplants or infected by HIV.
Chicken pox symptoms in adults
Although chicken pox symptoms in adults are similar to those exhibited by children, they tend to be more severe.
- Fever, body aches and headache can occur a day or two before the rash.
- Red spots appear and develop into itchy vesicles – first appearing on the trunk, face and scalp, then spreading over the entire body. When scratched, these spots may leave scars. Eventually, the blisters dry up and form crusts before healing.
Possible complications of chicken pox in adults
Complications resulting from chicken pox in adults can be due to the spread of the virus to other sites or to a superimposed infection by bacteria. These potential complications include:
- Bacterial infections of the skin, soft tissues, bones, joints or bloodstream (sepsis)
- Pneumonia
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
- Toxic shock syndrome
Read on to learn about shingles and what chicken pox does to pregnant women.
Ref: R14
Contributed by
Public Events
Get the Health Buddy App
© 2025 SingHealth Group. All Rights Reserved.














 Get it on Google Play
Get it on Google Play