Coronary artery disease (CAD) is caused by atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries due to old age. Experts from National Heart Centre Singapore give an overview of its causes and symptoms.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a silent killer.
"Many people with this disease (coronary artery disease) are not aware they have it, as it develops slowly and silently over decades. It can go virtually unnoticed until it produces a
heart attack," say doctors from
National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS), a member of the
SingHealth group.
Watch the video!
What is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as ischaemic heart disease, occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle (the coronary arteries) become hardened and narrowed.
The arteries harden and narrow due to a build-up of fatty deposits called plaque on their inner walls. The build-up of plaque is known as
atherosclerosis. As the plaque increases in size, the insides of the coronary arteries get narrower and less blood can flow through them.
Eventually, blood flow to the heart is reduced, which can cause chest pain (angina). A sudden, complete blockage can lead to a heart attack.
Read this article for ways to prevent and manage atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries).
Causes and symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease is caused by atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries due to old age. In atherosclerosis, plaque build-up in the arteries is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances from the blood.
Plaque build-up in the arteries often begins in childhood and over time, it can:
Narrow the arteries, reducing the amount of blood and oxygen reaching the heart.
Block the arteries completely which stops the flow of blood to the heart.
Cause blood clots to form which can block the arteries that supply blood to the heart.
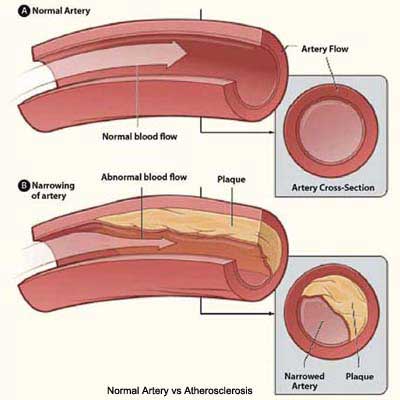
Above diagram: A normal artery with nomal blood flow and an artery containing plaque build-up.
CAD varies in signs and symptoms and in severity.
See next page for the
treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD).
Ref: V10
Check out other articles on heart health:
Tips for a Healthy Heart
Sudden Chest Pains You Shouldn't Ignore
Heart Palpitations: When Are They Serious?
How a Viral Infection Can Affect the Heart
How to Survive a Heart Attack When Alone
