Obesity is treatable with a non-surgical weight loss procedure called endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG). Dr Ravishankar Asokkumar, Consultant from the Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Singapore General Hospital (SGH) explains more.
Treating obesity
The main goal for treating obesity is to achieve >10-15% total body weight loss, improve quality of life and reduce mortality risk. Prior to Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG), options were either minimally effective like diet and lifestyle intervention or more invasive, like bariatric surgery, catering only to 1-2% of eligible patients with obesity.
What is Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG)
"Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is a non-surgical weight loss procedure performed to reduce the size of the stomach in patients with obesity. It is performed using an endoscope fitted with a suturing device at the tip," explained
Dr Ravishankar Asokkumar, Consultant from the
Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at
Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a member of the
SingHealth group.
In ESG, the stomach is inspected first, and then an endoscope fitted with a suturing device is introduced orally. Using the device and accessories, multiple full-thickness sutures are placed inside the gastric wall to make it smaller like a tube and reduce its distensibility.
This leads to significant weight loss by enabling the patients to feel full quickly after a meal and limiting their meal volume.
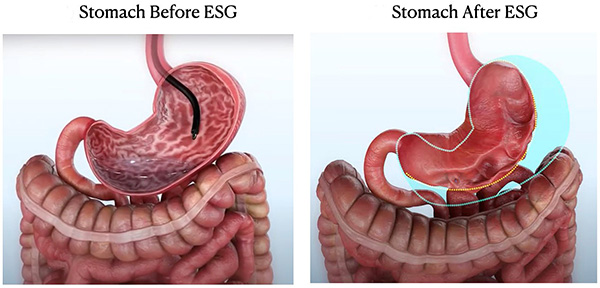
Image is courtesy of
Apollo Endosurgery, USA
How is endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) performed
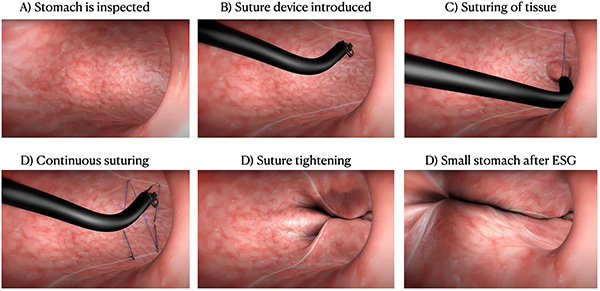
Image is courtesy of
Apollo Endosurgery, USA
ESG is performed under general anesthesia in an Endoscopy unit and takes approximately 60 minutes. After the procedure, the patient will need to stay in the hospital for 24 hours for observation.
As ESG is minimally invasive (not involving any incision or scar in the abdomen), the risk of complications is low, and patients can quickly return to their daily activity.
However, like any weight-loss procedure, commitment to a healthy lifestyle is required for long term success.
When combined with lifestyle modification, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) results in about 15% to 20% total body weight loss at 12 to 24 months.
Benefits of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG)
ESG is a less invasive procedure than surgery. By achieving the desired weight loss, patients can expect to lower their risk of obesity-related health problems like:
Who will benefit from endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG)?
ESG is suitable for
Obese patients (with BMI ≧27.5 kg/m2)
Patients who do not qualify for bariatric surgery
Patients who decline or are unsuitable for bariatric surgery
Those who are unsuccessful in achieving or maintaining weight loss after diet and lifestyle modification alone
Risks of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG)
ESG is a safe procedure. The risk of adverse events reported with ESG is around 1-2%. The most frequent symptoms after ESG are abdominal pain and vomiting. The symptoms can be managed with medications and usually resolves within a few days. Other uncommon adverse effects include:
Post-procedural bleeding,
Perforation (puncture through the wall of the stomach), and
Entrapment of the adjacent organs
Most of these complications can be managed via the endoscope and rarely require surgery. Only extremely rarely may these complications be fatal.
Obesity in Singapore
Obesity is a chronic disease. Compared to people with normal weight, it has been shown that being overweight and obese puts a person at increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and obstructive sleep apnea. It also increases risk of 13 different types of cancers and increased mortality.
It is estimated that the prevalence of obesity in Singapore is around 11% and is expected to go higher. Obesity is also the single largest contributor to the nation's disease burden of diabetes mellitus (73%).
Ref: K21
Other articles you may be interested in:
Our Ultimate Guide to Healthy Weight Loss
Getting Medical Help for Weight Loss
