Applying heat to a sprain or fracture will cause an increase in swelling and prevent an injury from healing.
Dr Lim Chin Siah, Consultant from the Department of Emergency Medicine at Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a member of the SingHealth group, shares 5 more facts and myths on home remedies.
5 more myths behind home remedies busted.
Myth 6: Clear a choking child’s throat with your fingers
Fact: Placing your fingers in a child’s throat can cause damage, or push the obstruction further down.
What to do: Stand behind the child and smack him or her between the shoulder blades with your hand, checking the mouth after each blow for the obstruction. Stop once you see the obstruction and remove it. You can do this up to five times. If this exercise doesn’t help, clench your fist and give up to five abdominal thrusts, thrusting above the navel in an upwards stroke, until the obstruction is dislodged from the throat.
Myth 7: Treat a black eye with a raw steak
Fact: The raw meat will only serve to infect the eye with any germs in the meat.
What to do: Apply ice wrapped in a clean towel to the eye area to reduce the swelling. Don’t place ice directly on the affected area since this can cause an ice burn, similar to a sunburn. See a doctor to check for head injuries.
Myth 8: Place a metal spoon into the mouth of a person having a seizure
Fact: This is intended to prevent the person from biting their tongue but it can do more harm than good; the metal spoon can cause damage to the teeth, palate or gums.
What to do: Place a blanket or coat on the floor and lie the person on it, turning the body sideways to prevent the tongue from blocking the airway. Keep the person in this position until the seizure stops.
Myth 9: Tie a tourniquet on an injured arm to stop bleeding
Fact: A tourniquet tied on an arm or leg will cut off the blood supply not just to the injured area but to the whole limb, which may cause tissue damage.
What to do: Apply direct pressure to the injured area with your hand, placing your hand over a sterile gauze or a clean towel, so that you disturb the wound as little as possible. Seek medical attention if the bleeding doesn’t stop.
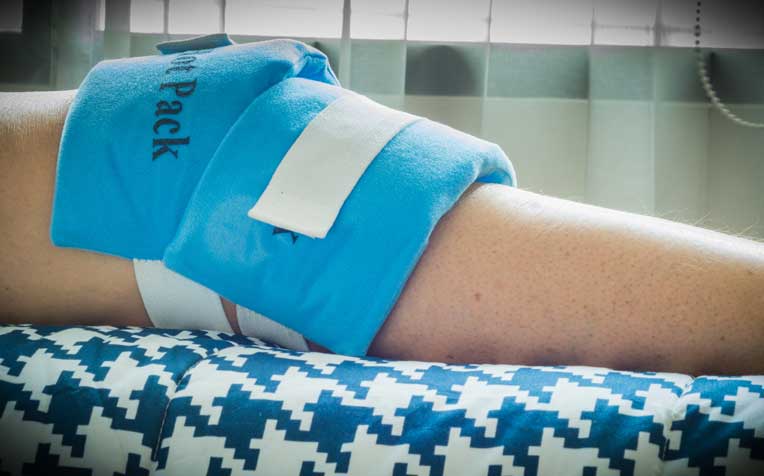
Myth 10: Apply heat to a sprain or fracture
Fact: Heat increases swelling and can prevent the injury from healing.
What to do: Apply an ice pack to the injury, and make sure the ice doesn’t touch the bare skin.
Ref: T12
Check out our other articles on first aid:
Home Emergency Kit: What Every Home Should Have
Burn Injuries: Treatment and Tips
Contributed by

















