HealthXchange will NEVER ask you to transfer money over a call. If in doubt, call the 24/7 ScamShield helpline at 1799, or visit the ScamShield website at www.scamshield.gov.sg.
Gout: Causes, Symptoms and Risk Factors
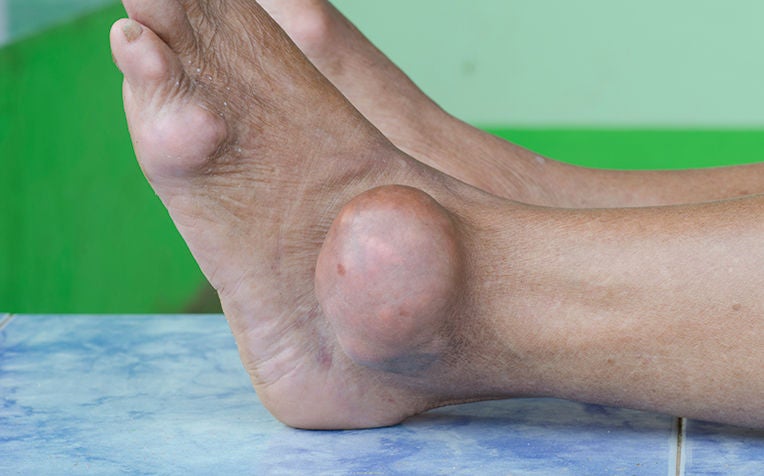
Gout attack is often a sudden and throbbing pain in the affected joint.
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes sudden, severe episodes of pain, tenderness, redness, warmth and swelling of the joints. It is the most common type of inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40. Women are usually protected from gout until after menopause.
Causes of gout
Gout is the result of deposits of needle-like crystals of uric acid in the joint spaces. Uric acid, a substance that results from the breakdown of purines in the body, usually dissolves in the blood and passes through the kidneys into the urine. In people with gout, the uric acid level in the blood becomes elevated. This is called hyperuricaemia and can be due either to the increased production of uric acid, eg. due to consumption of food rich in purines, or decreased excretion of uric acid from the kidney, eg. renal impairment.
Symptoms of gout
An attack often occurs very suddenly with the maximum intensity of pain reached within a few hours. The joint involved can be extremely painful and is often swollen, warm and red. This rapid development of joint pain is a feature that differentiates gout from most other forms of arthritis. The most common joint affected is the first joint of the big toe. Other joints that may be affected are the knee, ankle, foot, hand, wrist and elbow joints. The shoulder, hip joints and the spine are rarely affected.
Risk factors of developing gout
- Hyperuricaemia
- Most people with gout have hyperuricaemia although not all people with hyperuricaemia have gout.
- Being overweight
- Excessive food intake increases the body’s production of uric acid.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- Alcohol interferes with the excretion of uric acid from the body.
- Food with high purine content
- Use of certain medications such as:
- Diuretics
- Salicylates
- Cyclosporine
- Niacin
- Levodopa
- Start of a uric-acid lowering treatment
- Crash diet
- Joint trauma
- Surgery or sudden, severe illness
- Genes
Ref: S13
Also, check out our other gout articles:
Contributed by
Related Articles
Conditions & Treatments
Public Events
Get the Health Buddy App
© 2025 SingHealth Group. All Rights Reserved.

















 Get it on Google Play
Get it on Google Play