Burn injuries are classified according to the extent of damage done to your skin.
Burn injuries may be common, but its occurence may be significantly lowered through prevention efforts.
A burn is a common injury that is highly preventable. Most burn injuries occur in the home and are accidental in nature. Women and children are more likely to fall victim to a burn injury in the kitchen, while men may suffer a burn injury at the workplace.
“Prevention efforts can significantly lower the incidence of burns, especially in children,” says Ms Pamela Ng, Senior Occupational Therapist, Department of Occupational Therapy, Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a member of the SingHealth group.
Different types of burn injuries and their symptoms
There are many different types of burn injuries, and they are classified according to the source of the injury and the extent of skin damage.
- Thermal
These are caused by fire, explosions, steam, hot objects, hot liquids, etc.
- Flash: caused by explosions from gas or flammable liquids, thermal radiation.
- Flame: caused by exposure to prolonged and intense heat, such as a fire.
- Scald: caused by contact with hot liquids, such as water, oil. A scald is the most common type of burn injury in children and older adults.
- Contact: caused by contact with heated materials such as metals, glass or plastic.
-
Chemical
As a result of coming into contact with strong acids or alkaline substances.
- Electrical
Caused by electrical sources.
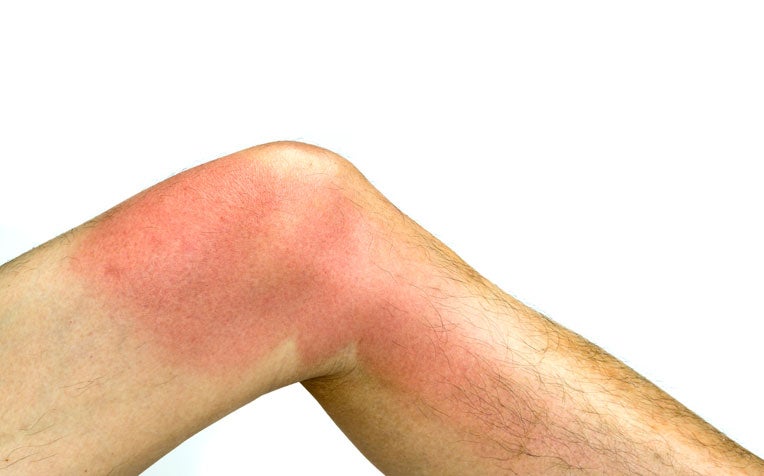
Burns are described as first-degree, second-degree or third-degree, depending on the extent of damage to the skin:
- Superficial (first-degree) burn
This involves the epidermis or top layer of the skin and is erythematous (red and inflamed), painful, and dry.
- Superficial partial thickness (superficial second-degree) burn
A second-degree burn affects the epidermis and part of the underlying dermis and has clear blisters and wet, erythematous skin. It blanches (skin appears paler than usual) and is painful when touched and generally does not cause scarring.
- Deep partial thickness (deep second-degree) burn This second-degree burn affects the deeper layers of the dermis, and appears white in colour. It does not blanch when touched and often results in scarring.
- Full thickness (third-degree) burn This is the most severe of burn injuries. All skin layers, including the underlying subcutaneous fat, are destroyed. This burn is dark brown or tan in colour and has a leathery feel. It is not sensitive to touch.
Read on to learn about tips and how to treat burns.
Ref: Q15
Contributed by













