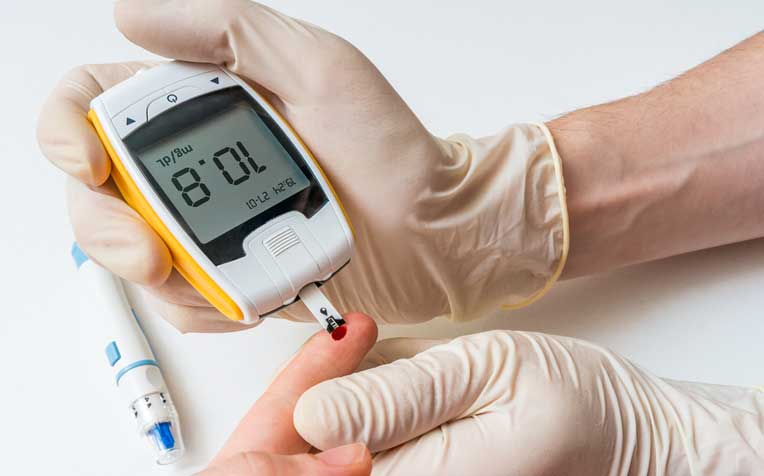
Gestational diabetes can be improved with lifestyle measures such as regular blood glucose monitoring.
How do you know you have gestational diabetes mellitus?
In Singapore, all pregnant women will be screened for gestational diabetes mellitus by means of an oral glucose tolerance test, between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
“The oral glucose tolerance test will be performed earlier in women who have high risk for gestational diabetes mellitus,” says Dr Lim Wei Ying, Associate Consultant, Department of Endocrinology, Singapore General Hospital, a member of the SingHealth group.
An oral glucose tolerance test would require:
- Fasting overnight (not eating or drinking anything apart from water)
- Blood test in the morning, followed by a 75g glucose drink
- Repeat blood glucose tests at 1 hour and 2 hours after the glucose drink
How is gestational diabetes mellitus treated?
When you have gestational diabetes mellitus, you will be under the care of a specialist healthcare team comprising of obstetricians, endocrinologists, specialised nurses, and dietitians.
Gestational diabetes mellitus usually improves with lifestyle measures such as:
- healthy eating
- exercise and
- regular blood glucose monitoring.
Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose levels will be taught, because it is important to ensure satisfactory glucose control during your pregnancy.
Despite best efforts at lifestyle modifications, some women need to take tablets or insulin injections to control their glucose levels. If insulin therapy is required, the technique for self -insulin injection will be taught.
Gestational diabetes mellitus treatment during pregnancy
During antenatal visits, ultrasound scans will be performed to monitor your baby’s growth closely. Regular blood tests will also be performed to monitor your blood glucose control. Individualised advice about timing and type of delivery will also be given to you by the specialist team.
During labour, it is essential for blood glucose levels to be controlled at a satisfactory level. Blood glucose levels will be measured every hour and some women may require an insulin drip for optimal glucose control.
Gestational diabetes mellitus treatment after childbirth
After you deliver your baby, your insulin requirement decreases significantly with rapid improvement of blood glucose levels.
Most patients, who require tablets or insulin injections during pregnancy, would be able to stop their medications. However, some women may have persistent diabetes mellitus after pregnancy.
Therefore, a repeat oral glucose tolerance test is needed for all women with gestational diabetes mellitus, about 6 to 12 weeks after delivery.
Are you at risk of gestational diabetes mellitus or diabetes mellitus in future?
Women with gestational diabetes mellitus have:
- a higher chance of having gestational diabetes mellitus in subsequent pregnancies, and also
- a 6-7 times higher chance of developing diabetes mellitus in future.
Tips to lower your risk of diabetes mellitus after pregnancy
Lifestyle measures such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercise have been shown to reduce the risk of diabetes mellitus by about 50%.
In addition to lifestyle measures, it is recommended that you:
- seek medical attention early for subsequent pregnancies, and
- have annual blood glucose tests as surveillance for diabetes mellitus.
Ref: O17
Contributed by

















 Get it on Google Play
Get it on Google Play