The insulin pump can deliver more precises doses of insulin, which is controlled by the user.
How does insulin pump therapy work?
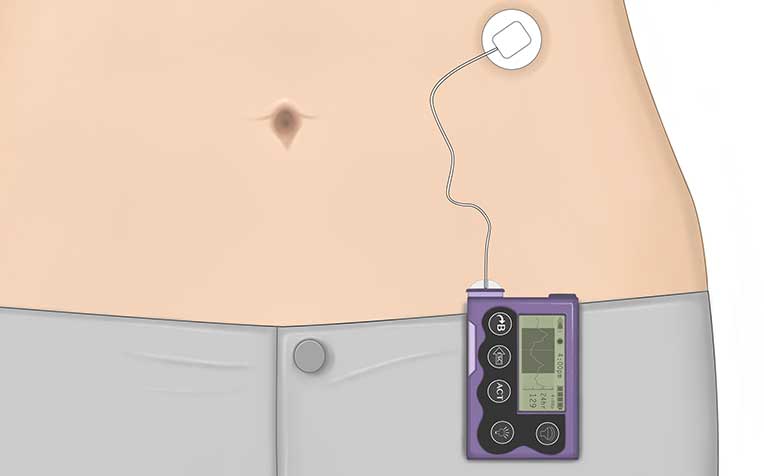
The insulin pump is a battery-operated device (see figure below), which contains a reservoir of quick-acting insulin that delivers both basal (background) and quick-acting insulin doses.
Importantly, the improved technology now allows programmable memory, the potential of multiple basal rates, and simple ways of titration and bolusing.

Insulin is delivered via an infusion set and cannula
into the subcutaneous layer of the abdomen.
An insulin pump can deliver insulin similar to a pancreas
"Whilst the insulin pump can deliver more precise doses of insulin, and in a manner more similar to a pancreas, the end user is still in ultimate control over insulin delivery. The pump uses quick-acting U-100 insulin that delivers both basal insulin 24 hours of the day, and bolus insulin," says Dr Daphne Su-Lyn Gardner, Consultant from the Department of Endocrinology, Singapore General Hospital (SGH), a member of the SingHealth group.
| The insulin pump first had its beginnings in the early 1960s as a massive backpack, created by Arnold Kadish of Los Angeles, California. It was not until 1978 that the first commercial insulin pump was launched, although the idea of lugging around a ‘Big Blue Brick’ which needed a screwdriver for insulin dose adjustment was neither practical nor attractive. It was not until the 1990s that advances in the field of medical device technology permitted the dramatic reductions in the size of the insulin pump to that of a handheld pager, allowing much greater portability. |
What is basal and bolus insulin?
Basal insulin
Basal insulin covers insulin requirements between meals and throughout the night. Each individual will require different amounts of basal insulin depending on factors like their weight and activity levels. With an insulin pump, the amount delivered can be adjusted by the hour to deliver varying amounts of insulin throughout the day.
For example, you may require greater amounts of insulin in the early morning hours than the rest of the day. Your pump will be programmed to deliver basal insulin at different rates in different time blocks to match your needs. Once programmed, these same rates continue everyday unless basal rates are altered.
Bolus insulin
Upon administering quick-acting U-100 insulin, it:
- Enters the bloodstream within 10-15 minutes
- Has the greater glucose-lowering effect for the first 1-1.5 hours
- Stops lowering glucose levels 4-5 hours later
Bolus insulin may be given to:
- Cover mealtime glucose rise from carbohydrates consumption (meal bolus)
- Correct high glucose levels (correction bolus)
Because the insulin pump only uses quick-acting insulin, there will be a quick rise in glucose levels (within 2 hours) if insulin infusion is interrupted. Insulin infusion should not be suspended/stopped for more than 1 hour without checking your blood glucose level.
What advantages does insulin pump therapy have over multiple daily injections?

Importantly, insulin pump does NOT deliver insulin automatically. The user is still in charge of the delivering the appropriate doses of bolus insulin according to the blood glucose level, and amending the basal rate according to his/her needs.
Insulin pump insertion sites

Insulin pump safety guidelines
There are important safety guidelines whilst using the insulin pump. Good safety practices are important to allow you to pre-empt and resolve potential problems promptly.
This includes:
- Checking your blood glucose levels regularly (minimum 3-4 times daily)
- Never ignoring a low glucose level (< 4.0 mmol/L) and keeping food/drink for hypoglycaemia treatment
- Never ignoring a high glucose level (> 13.0 mmol/L)
- Re-checking a blood glucose level after a low or high glucose reading to ensure these return to target range
Singapore General Hospital (SGH) has a structured pathway and multidisciplinary team in place for initiating and managing insulin pumps in adults. Please ask your healthcare provider if you are interested in finding out more about insulin pumps.
Ref: O17
Contributed by


















 Get it on Google Play
Get it on Google Play