HealthXchange will NEVER ask you to transfer money over a call. If in doubt, call the 24/7 ScamShield helpline at 1799, or visit the ScamShield website at www.scamshield.gov.sg.
Tips to Prevent Infections and Importance of Child Vaccination
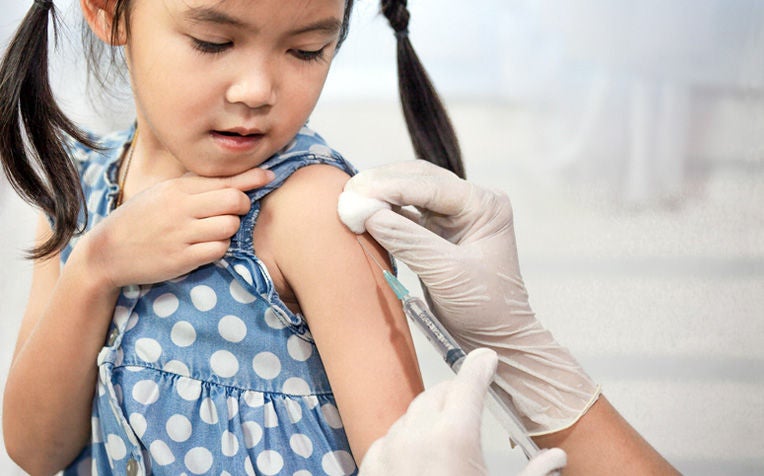
Vaccinations are still important to protect a child against harmful infectious diseases.
How to keep infections at bay
The best way to prevent falling prey to infectious diseases is to have good hygiene practices. Dr Jade Soh, Consultant from the Department of Infectious Diseases at Sengkang General Hospital (SKH), a member of the SingHealth group, shares some common precautions you can take.
1) Practise hand hygiene
Every family member, including adults, should wash their hands after coming home from outside, before and after they eat, after toileting, or if they accidentally touch the trash bins. Hand hygiene is the key to preventing common illnesses such as colds and Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD).
Also, avoid sending your children to kindergarten or childcare if there is an HFMD outbreak in school.
2) There's also home hygiene
Properly disinfect and clean with a focus on high-touch surfaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, taps, toilet flush handles and remote controls. Visit NEA’s website (here) for a list of household products for combating viruses including COVID-19.
3) Instill cough hygiene

Teach your child to cough or sneeze into a tissue to prevent the droplets and germs from ending up on others.
4) Mask up when ill
Wear a mask at home if you are sick and avoid sharing food or drinks with other family members.
Why vaccinations are important to build a child's immunity

Doctors advise parents not to forego vaccinations.
Vaccinations train your child’s immune system to make antibodies that protect them from harmful diseases.
Bring your children for all mandatory childhood vaccinations required by the government such as Hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps & rubella (MMR), etc.
Doctors also recommended getting vaccinated against pneumonia and meningitis (pneumococcal vaccine), chickenpox (varicella vaccine) and the influenza virus.
This article was adapted from Skoop magazine (issue 7).
Ref: L20
Check out other articles on vaccination:
Child Vaccination Schedule (from 15 months to 11 years old)
Pneumococcal Vaccination: Why Children Need It
Your Best Protection Against the Flu (Influenza)
Contributed by
Related Articles
Conditions & Treatments
Public Events
Get the Health Buddy App
© 2025 SingHealth Group. All Rights Reserved.


















 Get it on Google Play
Get it on Google Play