HealthXchange will NEVER ask you to transfer money over a call. If in doubt, call the 24/7 ScamShield helpline at 1799, or visit the ScamShield website at www.scamshield.gov.sg.
Common Knee Injuries: Knee Osteoarthritis
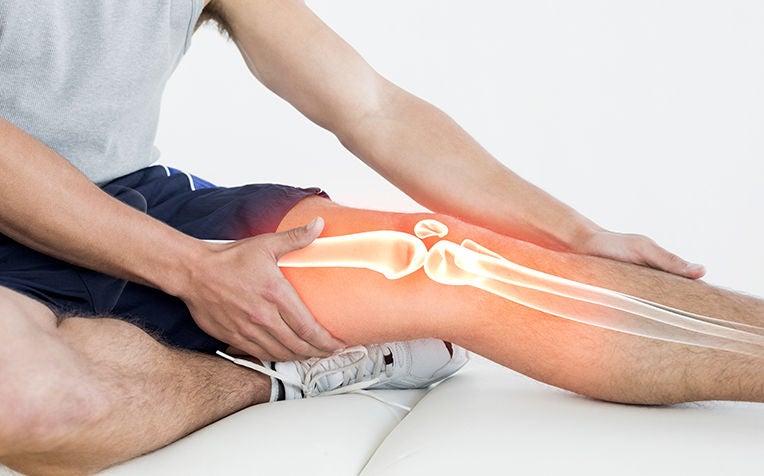
Knee osteoarthritis is a common cause of disability.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help to manage the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis.
Treatment for knee osteoarthritis
For the treatment of knee osteoarthritis, your doctor may sometimes recommend a steroid injection into or around the joint. The pain relief is usually only temporary, and your doctor will limit the number of steroid injections that you can receive.
Another type of injection therapy is called visco-supplementation. This involves the injection of hyaluronic acid derivatives into the joint. Hyaluronic acid is a normal component of joint fluid. However, the response to hyaluronic acid injection, as with steroid injection, is variable and usually temporary.
Watch this video to find out more about knee osteoarthritis - learn to prevent, and watch how it's treated!
Surgery for knee osteoarthritis
Surgery is usually only offered for severe cases that have not responded to other forms of therapy. Both the type of surgery and the decision for surgery are made following careful discussions between you and your doctor. Some of the more common types of surgery include:
Arthroscopy
- Arthroscopy is suitable for early knee osteoarthritis, and is considered a minor procedure during which the orthopaedic specialist uses an ‘arthroscope’ to look inside the joint.
- Arthroscopy is a form of ‘keyhole surgery’. During the procedure, the surgeon will be able to clean up damaged portions of the joint, or stimulate repair in areas where the cartilage has been lost.
Osteotomy
- Osteotomy is suitable for younger patients (generally less than 50 years of age) with limited knee osteoarthritis. During osteotomy, the bones around the joint are cut to allow the alignment of the joint to be corrected. Symptom relief can sometimes be achieved for up to 10 years following this procedure.
Joint replacement
In late stages of osteoarthritis, the joint becomes so damaged that the best treatment is to replace it with an artificial one, which is typically made of a metal alloy together with a plastic component. The entire joint may be replaced (total joint replacement), or if osteoarthritis is limited to only one part of the joint, then the surgeon may choose to only replace that part (unicompartmental / partial joint replacement).
Ref: S13
Also, check out our other articles on pain of the leg and feet:
Knee Osteoarthritis (OA Knee): Symptoms, Tips, Treatment and Exercises
Home Remedies for Knee Pain and Shin Splints
Runner's Knee: What It Is and How to Prevent
Tips to Prevent Common Running Injuries
Contributed by
Related Articles
Conditions & Treatments
Public Events
Get the Health Buddy App
© 2025 SingHealth Group. All Rights Reserved.


















 Get it on Google Play
Get it on Google Play